Videos
Khan Academy
Stellar distance using parallax
Stellar parallax clarification
Crash Course Astronomy
The Sun: Crash Course Astronomy #10
Light: Crash Course Astronomy #24
Distances: Crash Course Astronomy #25
Stars: Crash Course Astronomy #26
Low Mass Stars: Crash Course Astronomy #29
White Dwarfs & Planetary Nebulae: Crash Course Astronomy #30
High Mass Stars: Crash Course Astronomy #31
Neutron Stars: Crash Course Astronomy #32
Black Holes: Crash Course Astronomy #33
Binary and Multiple Stars: Crash Course Astronomy #34
Star Clusters: Crash Course Astronomy #35
Nebulae: Crash Course Astronomy #36
The Milky Way: Crash Course Astronomy #37
Galaxies, part 1: Crash Course Astronomy #38
Galaxies, part 2: Crash Course Astronomy #39
Gamma-Ray Bursts: Crash Course Astronomy #40
Dark Matter: Crash Course Astronomy #41
The Big Bang, Cosmology part 1: Crash Course Astronomy #42
Dark Energy, Cosmology part 2: Crash Course Astronomy #43
A Brief History of the Universe: Crash Course Astronomy #44
Deep Time: Crash Course Astronomy #45
Planet Hunters
What does stellar variability look like for different types of stars?
How do you estimate a star’s mass and radius using asteroseismology?
Terms
Hayashi tracks (and Henyey tracks)
Proto-Stars –
– YSO : Young Stellar Objects – comprise two groups – 1) proto-stars and 2) pre-main sequence stars
– PMS : Pre-Main Sequence
https://home.ifa.hawaii.edu/users/jpw/classes/star_formation/lectures/protostars.pdf
spectral index
http://astro.vaporia.com/start/spectralindex.html
young stellar object
http://astro.vaporia.com/start/yso.html
HR Diagrams – Main Sequence Stars
https://homepage.physics.uiowa.edu/~pkaaret/s09/L12_starsmainseq.pdf
Objects
Carina (sh): HD 95086, NGC 3324
Cygnus (nh): V1057 Cygni
Dorado (sh): 30 Doradus (Tarantula Nebula)
Libra (sh): HD 141569
Musca (sh): HD 100546
Ophiuchus (equator): Barnard 68
Orion (equator): FU Orionis, HOPS 383, M42 (Orion Nebula)
Pegasus (nh): Stephan’s Quintet
Perseus (nh): NGC 1333
Sextans (equator) : Baby Boom Galaxy
Taurus (nh): HL Tauri, L1527, NGC 1555
Volan (sh): J122051 – 491255 (typo in one of the pictures on NASA website)
Galaxy Characteristics
Dark Matter – The First Clue – velocity of stars orbiting a galaxy – SIWH !!! [Link]
The Universe the Beginning and the maybe the end
Time Line of the Universe [Link]
Cosmic Inflation [Link]
Telescopes
JWST (James Webb Space Telescope)
Wikipedia [Link1]
WEBB Space Telescope home page [Link2]
NASA – James Webb page [Link3]
Hubble
Wikipedia [Link]
Spitzer
Wikipedia [Link]
Chandra (X-ray)
Wikipedia [Link]
Roman Space Telescope
Wikipedia [Link]
ALMA
Wikipedia [Link]
ALMA Home Page [Link]
VLA
Wikipedia [Link]
NRAO VLA Home Page [Link]
Equations that come in handy –
Parallax Distance Equation
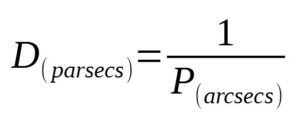
Distance Modulus Equation (D is in parsecs)
mapparent magnitude = Mabsolute magnitude – 5 + 5 * log(D)
Newton’s version of Kepler’s Third Law
P –> period in Earth years
A –> average distance between objects in AU (astronomical units)
M’s –> solar masses
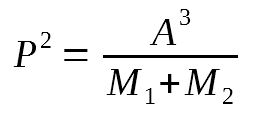
Via-Viva Equation (smaller mass is insignificant) (not so handy)